Using Feeding Tubes
Feeding tubes can be an effective way to provide your child with the nutrition that they need to stay healthy.
Not all children will go home from the hospital with a feeding tube, but it can be a beneficial solution for children who are struggling to take a bottle or are having trouble gaining weight.
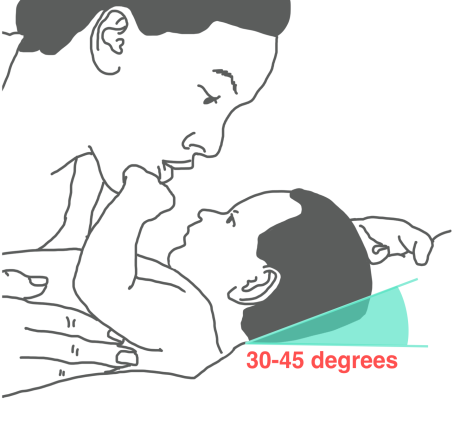
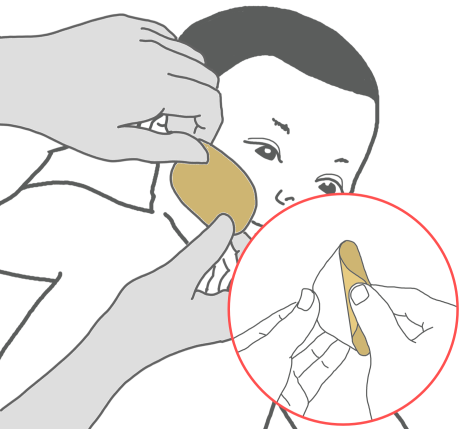
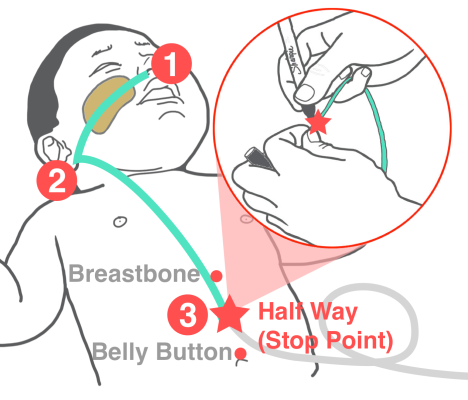
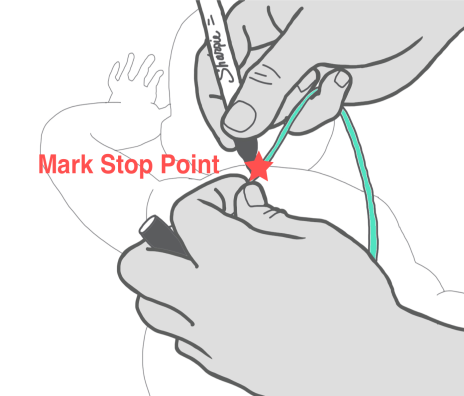
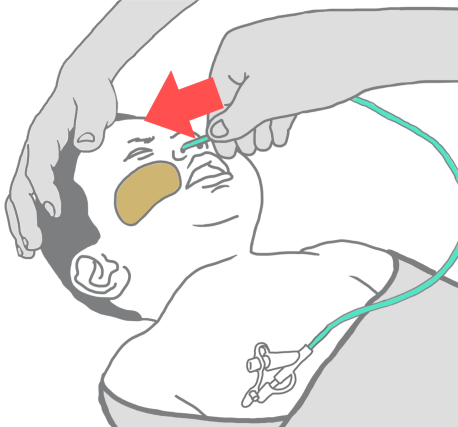
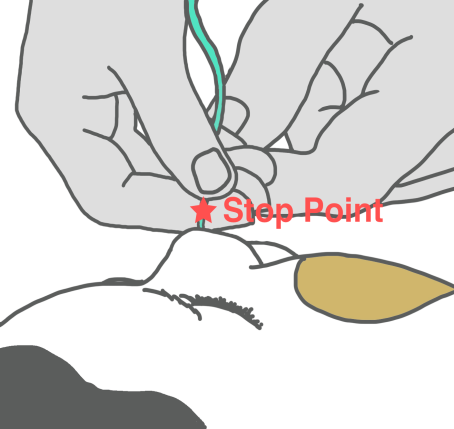
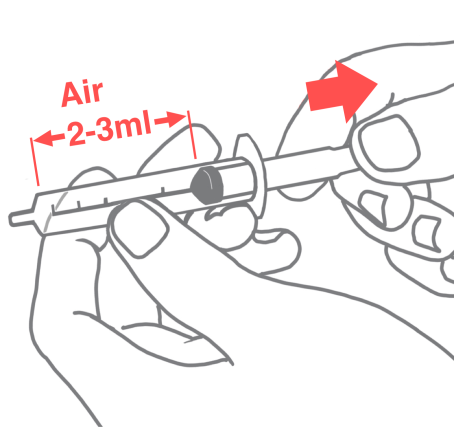
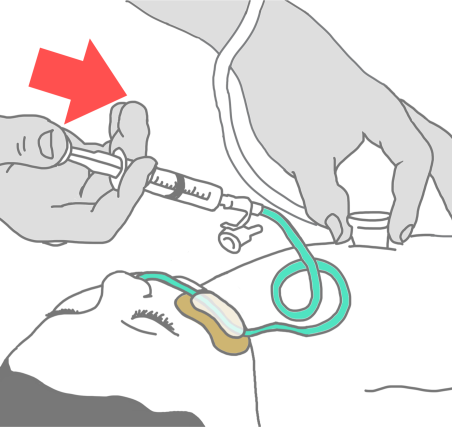
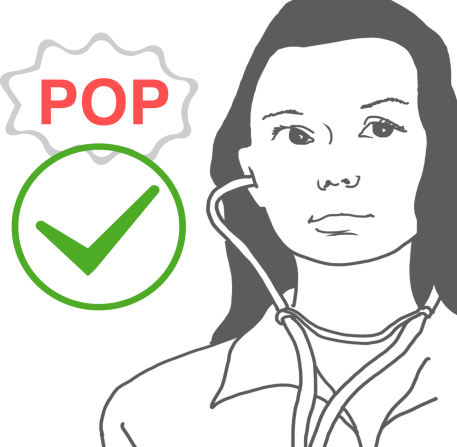
Ask your nurse for a step-by step information sheet on how to insert an NG tube.
Here are some common types of feeding tubes:
- Nasogastric (NG) Tube
- Nasojejunal (NJ) Tube
- Orogastric Tube
- Jejunostomy (J) Tube
- Gastrojejunal (GJ) Tube
- Gastrostomy (G) Tube
For an instructional video on how to insert an NG tube: www.cincinnatichildrens.org/ health/f/silastic-feeding-tube